Data connections via a fiber are simple to comprehend, requiring laser transceivers and fiber connectors at each end. Moving on from these fundamentals connections in data centers can be very complicated. Appreciating the service levels and ownership at each step can make or break a good data center roll out:
1) Types of Data Centers and Connections
- Owned Data Centers – Businesses that own and operate their own data center are responsible for all the management of the fiber optic connections. Data Center Interconnect is the connection between two or more, separately located data centers provided by a carrier, or via leased, or owned fiber by the data center. Campus cross-connects are a physical link between servers, routers, switches, or other equipment. However, instead of existing within one building, the connection is made between two geographically separate buildings.
- Hosted and Cloud Data Centers – They provide data processing, and bandwidth which is packaged into a consumption-based pricing model or a monthly fee. The data center oversees all of the fiber optics connections from rack to the carrier separation point. Providing customer with a direct fiber connection to their cloud service provider and removes the need for data to travel via public links between the cloud provider and the customer.
- Colocation Data Centers – These provide a wide variety of services that begin with floor space, power, and bandwidth. Plus, they use numerous tenants under one roof to maximize the significant resources required to effectively operate a data center. Fiber optic connections in colocation data centers are more complicated, as the data center may manage physical fiber level ‘Cross-Connects” between a tenant and a carrier or a tenant and another tenant. This underlines the importance of making the correct choices for fiber optic connectivity. Colocation data centers can be carrier owned, or carrier neutral. Carrier neutrals have physical fiber connections with two or more “On-net” service providers. In addition, other third-party service providers may provide fiber to the data center to service customers. This differs from a data center which is served exclusively by one service provider.
- Carrier Hotel – This is a building with fiber connections to numerous service providers where inter connection between two or more providers can be created. It is not a data center.
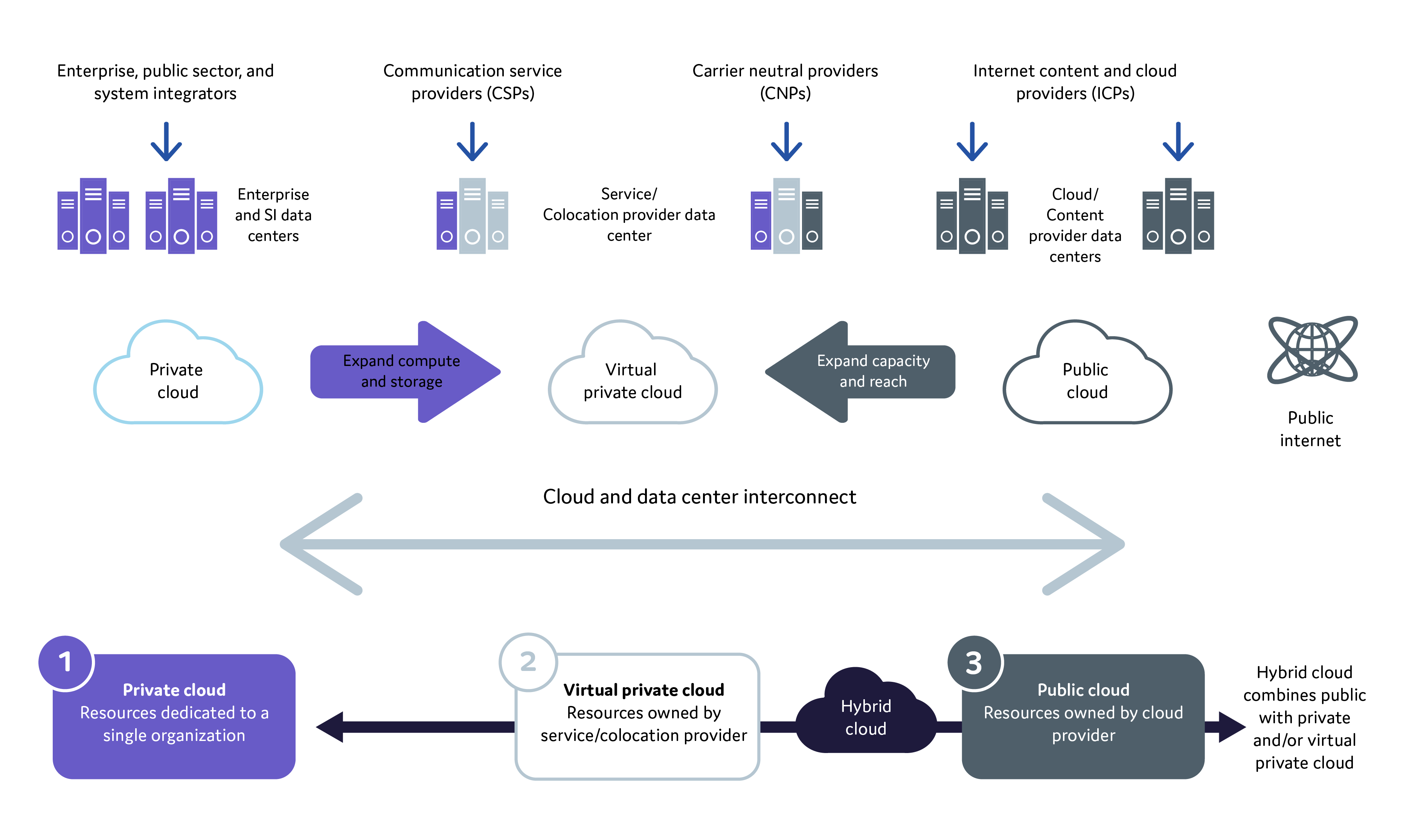
2) Fiber Ownership
There is an important difference between who owns or leases the fiber. The primary fiber providers include the following organizations:
- Internet Content Providers – More companies such as Google, Facebook, Microsoft, Akami and Alibaba are now building their own fiber infrastructure to support content collection, analysis, and distribution.
- Service Providers – Typically they are the telecommunications or cable companies e.g. Verizon, Deutch Telecom, Tata, Tata, or Comcast.
- Dark Fiber Providers – Various companies such as Crown and Castle, eunetworks, and Zayo, lease fiber to others. Leases are called Indefeasible Right of Use (IRU) and grant the lessor exclusive right to the fiber.
3) Technical Specifications
There is a broad mixture of technical parameters needed for these connections. Fiber connections are usually agnostic to the upper layer protocols that traverse the connection, but they are typically specified and may even define the connection type. A limited list of specifications that may be required includes:
1. Type, length, or loss of fiber
2. Data rate
3. Connector
4. Wavelength
5. Transceiver (e.g. coherent, PAM)
6. Other cables (AOC, DOC)
7. Layer 2 service
8. Layer 3 service
Typically, there are numerous transceiver choices for each connection type. ProLabs has the experience and the knowledge to help customers understand the many trade-offs. The most common transceivers for data center links are the SFP, SFP+ and QSFP+ form factors, these typically connect over longer distances. The reach, data rate, connector type, wavelength and operating temperature will be relevant to making the optimal selection.
Fiber connections within the data center may present the widest range of options for both transceivers and the AOC/DOC cables used to create efficient fiber architectures within the building.
Whatever your connection type, ProLabs can provide you with both the expertise and the inventory to deliver the best solution for your business.


